DOSING VIDEO
Learn more about OPDIVO + chemotherapy synchronized dosing options in mUGI cancers with Dr. Misagh Karimi

OPDIVO Qvantig™ (nivolumab + hyaluronidase-nvhy) is approved as a subcutaneous injection
In the 1L treatment of mUGI Cancer
‡Fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemo.1 §Based on Checkmate 649 5-year follow-up analysis (minimum follow-up 60.1 months). In PD-L1 CPS ≥5, mOS was 14.4 mos (95% CI: 13.1–16.2) with OPDIVO + chemo vs 11.1 mos (95% CI: 10.1–12.1) with chemo alone (HR=0.71; 95% CI: 0.61–0.81). In PD-L1 CPS ≥1, mOS was 13.8 mos (95% CI: 12.4–14.8) with OPDIVO + chemo vs 11.4 mos (95% CI: 10.7–12.3) with chemo alone (HR=0.76; 95% CI: 0.67–0.85). At primary analysis (minimum 12.1-month follow-up), mOS in PD-L1 CPS ≥1 was 14.0 mos (95% CI: 12.6–15.0) with OPDIVO + chemo vs 11.3 mos (95% CI: 10.6–12.3) with chemo alone (HR=0.77; 95% CI: 0.68–0.88; P<0.0001).1,3 IIChemo with placebo or other agents. ¶Based on median follow-up of 71.3 months (minimum 60.1 months) in Checkmate 649.2,4 #In Checkmate 648, based on a 13.0-month primary analysis, mOS in PD-L1 TC ≥1% was 15.4 mos (95% CI: 11.9–19.5) with OPDIVO + chemo vs 9.1 mos (95% CI: 7.7–10.0) with chemo alone (HR=0.54; 95% CI: 0.41–0.71; P<0.0001). At 4-year follow-up (minimum follow-up 45.1 months), mOS in PD-L1 TC ≥1 was 15.0 mos (95% CI: 11.9–18.7) with OPDIVO + chemo vs 9.1 mos (95% CI: 7.7–10.0) with chemo alone; (HR=0.60; 95% CI: 0.47–0.77).1,4,5
CHECKMATE 649
*OPDIVO® (nivolumab), in combination with fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemotherapy, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, gastroesophageal junction cancer, and esophageal adenocarcinoma whose tumors express PD-L1 (≥1%).
CHECKMATE 648
†OPDIVO, in combination with fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemotherapy, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with unresectable advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) whose tumors express PD-L1 (≥1%).
1L=first-line; CI=confidence interval; CPS=combined positive score; EAC=esophageal adenocarcinoma; GC=gastric cancer; GEJC=gastroesophageal junction cancer; HR=hazard ratio; I-O=immuno-oncology; mOS=median overall survival; mos=months; mUGI=metastatic upper gastrointestinal; PD-L1=programmed death-ligand 1; TC=tumor cell.
*Fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemotherapy.1 In Checkmate 649: OPDIVO + FOLFOX and OPDIVO + CapeOx; in Checkmate 648: OPDIVO + cisplatin and 5-FU.1
5-FU=5-fluorouracil; CapeOx=capecitabine and oxaliplatin.
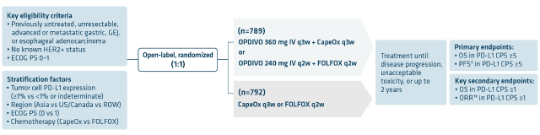
CHECKMATE 649: IN PATIENTS EXPRESSING PD-L1 CPS ≥1 WITH ADVANCED OR METASTATIC NON-HER2+ GASTRIC CANCER, GEJ, AND ESOPHAGEAL
ADENOCARCINOMAS
*mFOLFOX6 (leucovorin, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin) regimen was given in Checkmate 649.1
†Assessed using blinded independent central review (BICR).1
‡Based on confirmed response.
CapeOx=capecitabine and oxaliplatin; CNS=central nervous system; ECOG PS=Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status; FDA=US Food and Drug Administration; GEJ=gastroesophageal junction; HER2=human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; IHC=immunohistochemistry; IV=intravenous; ORR=overall response rate; OS=overall survival; PFS=progression-free survival; q2w=every 2 weeks; q3w=every 3 weeks; q4w=every 4 weeks; ROW=rest of world; UGI=upper gastrointestinal.
LIMITATION: The 60-month follow-up analyses were not statistically powered and cannot detect differences between treatment arms.2,5
Primary analysis (12.1-month minimum follow-up): secondary endpoints in PD-L1 CPS ≥1 population (n=1296)1
Primary analysis: dual primary endpoints in the PD-L1 CPS ≥5 population (n=955)1
Extended follow-up at 5 years2
*Vs chemotherapy alone.1
†FOLFOX or CapeOx.1
‡Assessed using blinded independent central review (BICR).1
mPFS=median progression-free survival.
Serious Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 649, serious adverse reactions occurred in 52% of patients treated with OPDIVO in combination with chemotherapy (n=782). The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with OPDIVO in combination with chemotherapy were vomiting (3.7%), pneumonia (3.6%), anemia (3.6%), pyrexia (2.8%), diarrhea (2.7%), febrile neutropenia (2.6%), and pneumonitis (2.4%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 16 (2.0%) patients who were treated with OPDIVO in combination with chemotherapy; these included pneumonitis (4 patients), febrile neutropenia (2 patients), stroke (2 patients), gastrointestinal toxicity, intestinal mucositis, septic shock, pneumonia, infection, gastrointestinal bleeding, mesenteric vessel thrombosis, and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Please see additional Important Safety Information below.
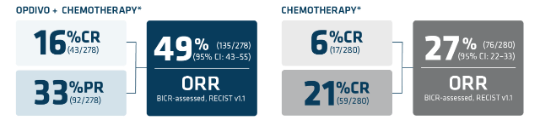
Primary analysis (12.1-month follow-up) in patients with PD-L1 CPS ≥11*†
*Assessed using the blind independent central review (BICR).1
†Based on confirmed response.1
‡Secondary endpoint.5
§FOLFOX or CapeOx.1
IIAn exploratory endpoint.5
CR=complete response; ITT=intention to treat; mDOR=median duration of response; PR=partial response; RECIST=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors.
Common Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 649, the most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in patients treated with OPDIVO in combination with chemotherapy (n=782) were peripheral neuropathy (53%), nausea (48%), fatigue (44%), diarrhea (39%), vomiting (31%), decreased appetite (29%), abdominal pain (27%), constipation (25%), and musculoskeletal pain (20%).
Please see additional Important Safety Information below.
OPDIVO is still available as an IV infusion. View OPDIVO IV dosing schedule >
INDICATION OPDIVO Qvantig (nivolumab + hyaluronidase-nvhy), as monotherapy, is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of completely resected esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer with residual pathologic disease in adult patients who have received neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (CRT).
INDICATION OPDIVO QVANTIG, in combination with fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemotherapy, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, gastroesophageal junction cancer, and esophageal adenocarcinoma whose tumors express PD-L1 (≥1).
*Fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemotherapy.1,8
†FOLFOX and CapeOx can be synchronized when used q2w and q3w, respectively.1,8
Learn more about OPDIVO + chemotherapy synchronized dosing options in mUGI cancers with Dr. Misagh Karimi

CHECKMATE 648: IN THE 1L TREATMENT OF ADULT PATIENTS EXPRESSING PD-L1 CPS ≥1 WITH METASTATIC ESOPHAGEAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
*Checkmate 648 included a third arm: OPDIVO 3 mg/kg IV q2w + ipilimumab 1 mg/kg IV q6w; n=325. The trial was not designed to compare OPDIVO + chemotherapy to OPDIVO + ipilimumab. Please refer to the full U.S. Prescribing Information for further information.1,7
†OPDIVO 240 mg IV on Days 1 and 15 of a 4-week cycle.1
‡Fluorouracil 800 mg/m2/day IV on Days 1 through 5 (for 5 days) and cisplatin 80 mg/m2 IV on day 1 (of a 4-week cycle).1
§Patients could receive OPDIVO plus ipilimumab until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years.1
¶Assessed using blinded independent central review (BICR).1
1L=first-line; CPS=combined positive score; ECOG PS=Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status; IHC=immunohistochemistry; IV=intravenous; ORR=overall response rate; OS=overall survival; PD-L1=programmed death-ligand 1; PFS=progression-free survival; ROW=rest of world; q2w=every 2 weeks; q4w=every 4 weeks; q6w=every 6 weeks.
§LIMITATIONS:
Dual primary endpoints in the PD-L1 TC ≥1% population (n=315)1
31% reduction in the risk of death with OPDIVO + chemotherapy† vs chemotherapy1
Extended follow-up at 45 months3
*Vs chemotherapy alone.1
†Fluorouracil and cisplatin.1
‡Minimum follow-up 45.1 months.3
||Assessed using blinded independent central review (BICR).1
CI=confidence interval; HR=hazard ratio; mOS=median overall survival; mPFS=median progression-free survival; NS=not significant.
Serious Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 648, serious adverse reactions occurred in 62% of patients receiving OPDIVO in combination with chemotherapy (n=310). The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients who received OPDIVO with chemotherapy were pneumonia (11%), dysphagia (7%), esophageal stenosis (2.9%), acute kidney injury (2.9%), and pyrexia (2.3%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 5 (1.6%) patients who received OPDIVO in combination with chemotherapy; these included pneumonitis, pneumatosis intestinalis, pneumonia, and acute kidney injury.
Please see additional Important Safety Information below.
Exploratory analysis in PD-L1 CPS ≥1 (minimum follow-up 13.0 months)1‡§II
In the primary analysis of PD-L1 ≥1%, ORR‡§ was 53% (95% CI: 45-61 [CR: 17%; PR 37%]) with OPDIVO + chemotherapy* vs 20% (95% CI: 14-27 [CR: 5%; PR 15%]) with chemotherapy alone. mDOR§|| was 8.4 mos (95% CI: 6.9-12.4; range: 1.4+ to 34.6+) with OPDIVO + chemotherapy* vs 5.7 mos (95% CI: 4.4-8.7; range: 1.4+ to 31.8+).
*Fluorouracil and cisplatin.1
†Minimum follow-up 45.1 months.3
‡Secondary endpoint.1
§Assessed using blinded independent central review (BICR).1
||An exploratory endpoint.7
BICR=blinded independent central review; CR=complete response; mDOR=median duration of response; PR=partial response; RECIST=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors.
Common Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 648, the most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in patients treated with OPDIVO in combination with chemotherapy (n=310) were nausea (65%), decreased appetite (51%), fatigue (47%), constipation (44%), stomatitis (44%), diarrhea (29%), and vomiting (23%).
Please see additional Important Safety Information below.
OPDIVO is still available as an IV infusion. View OPDIVO IV dosing schedule >
INDICATION OPDIVO QVANTIG, in combination with fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-containing chemotherapy, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with unresectable advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) whose tumors express PD-L1 (≥1).
Limitations of Use: OPDIVO QVANTIG is not indicated in combination with ipilimumab for the treatment of patients with unresectable advanced or metastatic ESCC.
*A 3-5 minute injection time of OPDIVO Qvantig compared to 30-minute infusion time of OPDIVO. This does not account for all aspects of treatment and does not include observation time. Actual clinic time may vary.
View a selected safety profile of adverse reactions seen in clinical trials.
Find dosing information to get patients started on therapy.
Learn more about other gastroesophageal indications across adjuvant and 1L metastatic settings.
References: