CHECKMATE 77T INDICATION: OPDIVO® (nivolumab), in combination with platinum-doublet chemotherapy, is indicated for the neoadjuvant treatment of adult patients with resectable (tumors ≥4 cm or node positive) NSCLC and no known epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations or anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements, followed by single-agent OPDIVO as adjuvant treatment after surgery.
CHECKMATE 816 INDICATION: OPDIVO, in combination with platinum-doublet chemotherapy, is indicated as neoadjuvant treatment of adult patients with resectable (tumors ≥4 cm or node positive) NSCLC.
CHECKMATE 77T: NEOADJUVANT OPDIVO + CHEMO FOLLOWED BY ADJUVANT OPDIVO AFTER SURGERY
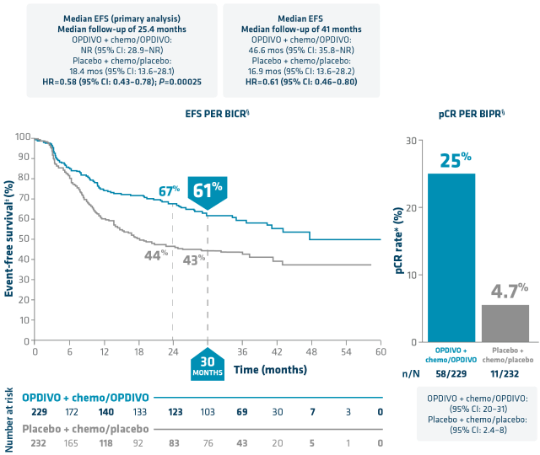
OPDIVO is the ONLY FDA-approved I-O therapy to both provide 1 in 4 patients a chance at pCR* and demonstrate a significant EFS benefit2-4†‡
EFS: Minimum/median follow-up: 31.3/41.0 months.4
pCR: Minimum/median follow-up: 15.7/25.4 months.3
Limitation: The pCR rate was assessed in a descriptive analysis of a prespecified secondary endpoint; the statistical testing plan did not assign alpha control to this endpoint, so direct comparisons between the treatment arms cannot be made.
*pCR by BIPR is defined as 0% residual viable tumor cells in both the primary tumor (lung) and sampled lymph nodes.3,8
†vs chemo with placebo.2,3
‡EFS per BICR is defined as time from randomization to disease progression that precludes surgery, abandoned surgery owing to unresectability, disease progression or recurrence after surgery, progression or recurrence for patients without surgery, or death due to any cause.2,3,8
§In patients with stage IIA–IIIB NSCLC, as determined by the 8th edition American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging criteria.2,3
I-O=immuno-oncology.
CHECKMATE 77T: NEOADJUVANT OPDIVO + CHEMO FOLLOWED BY ADJUVANT OPDIVO AFTER SURGERY
An observed trend toward higher OS rates4*
Minimum/median follow-up: 31.3/41.0 months4
Limitation: OS data (HR=0.85 [95% CI: 0.61–1.18]) were immature at the prespecified interim analysis and did not cross the boundary for statistical significance. These results should be interpreted with caution.
- EFS is a primary endpoint and pCR and OS are secondary endpoints3
*vs chemo with placebo.4
Select Important Safety Information
Serious Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 77T, serious adverse reactions occurred in 21% of patients who received OPDIVO in combination with platinum-doublet chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment (n=228). The most frequent (≥2%) serious adverse reactions was pneumonia. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 2.2% of patients, due to cerebrovascular accident, COVID-19 infection, hemoptysis, pneumonia, and pneumonitis (0.4% each). In the adjuvant phase of Checkmate 77T, 22% of patients experienced serious adverse reactions (n=142). The most frequent serious adverse reaction was pneumonitis/ILD (2.8%). One fatal adverse reaction due to COVID-19 occurred.
Common Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 77T, the most common adverse reactions (reported in ≥20%) in patients receiving OPDIVO in combination with chemotherapy (n=228) were anemia (39.5%), constipation (32.0%), nausea (28.9%), fatigue (28.1%), alopecia (25.9%), and cough (21.9%).
Surgery Related Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 77T, 5.3% (n=12) of the OPDIVO-treated patients who received neoadjuvant treatment, did not receive surgery due to adverse reactions. The adverse reactions that led to cancellation of surgery in OPDIVO-treated patients were cerebrovascular accident, pneumonia, and colitis/diarrhea (2 patients each).
Please see additional Important Safety Information below.
INDICATION OPDIVO Qvantig (nivolumab + hyaluronidase-nvhy), in combination with platinum-doublet chemotherapy, is indicated for the neoadjuvant treatment of adult patients with resectable (tumors ≥4 cm or node positive) NSCLC and no known epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations or anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements, followed by OPDIVO Qvantig as monotherapy in the adjuvant setting after surgical resection.
- OPDIVO Qvantig is administered as a 3- to 5-minute subcutaneous injection1
- Refer to the respective Prescribing Information for each therapeutic agent for the recommended dosage and administration information as appropriate
- Administer OPDIVO Qvantig first, followed by platinum-doublet chemo on the same day1*
- No premedication required with OPDIVO Qvantig1
*Every 3 weeks until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or for up to 4 cycles.1,2
†Platinum-doublet chemotherapy consisted of one of the following: Paclitaxel 175 mg/m2 or 200 mg/m2 and carboplatin AUC 5 or AUC 6 (any histology); pemetrexed 500 mg/m2, and cisplatin 75 mg/m2 or carboplatin AUC 5 or AUC 6 (nonsquamous histology); or cisplatin 75 mg/m2 and docetaxel 75 mg/m2 (squamous histology).1,2
Pt=platinum.
Perioperative OPDIVO: Studied in patients with stage IIA-IIIB NSCLC2,3,8,10
- Primary endpoint2,3,8:
- EFS (by BICR): Time from randomization to disease progression that precludes surgery, abandoned surgery owing to unresectability, disease progression or recurrence after surgery, progression or recurrence for patients without surgery, progression for patients without surgery, or death due to any cause
- Select prespecified secondary endpoint3,8:
- pCRII (by BIPR): 0% residual viable tumor cells in both the primary tumor (lung) and sampled lymph nodes
- The medium number of adjuvant doses received was 13 (range: 1–13) in both OPDIVO + chemo/OPDIVO and placebo + chemo/placebo arms11
*EGFR testing was mandatory in all patients with NSQ histology. ALK testing was done in patients with a history of ALK alterations. EGFR/ALK testing done using US FDA/local health authority–approved assays.10
†Determined by the PD-L1 IHC 28-8 pharmDx assay (Dako).10
‡NSQ: cisplatin + pemetrexed, carboplatin + pemetrexed, or carboplatin + paclitaxel; SQ: cisplatin + docetaxel or carboplatin + paclitaxel.10
§Until disease progression, recurrence, unacceptable toxicity or for up to 1 year (13 cycles) post-surgery.2,8
∥Assessed per immune-related pathologic response criteria.10
ECOG PS=Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; IHC=immunohistochemistry.
Checkmate 77T baseline characteristics3,11
Percentages may not total 100 due to rounding.
*One patient had EGFR mutation and ALK translocation.11
†Five patients (2.2%) in the OPDIVO + chemo/OPDIVO group and 6 patients (2.6%) in the placebo + chemo/placebo group switched from cisplatin to carboplatin. Neoadjuvant platinum chemotherapy was not reported in 2 patients (0.9%) in the OPDIVO + chemo/OPDIVO group and 4 patients (1.7%) in the placebo + chemo/placebo group.3
‡Disease stage (per AJCC 8th edition) as reported in case report forms. Two (1%) patients in the OPDIVO + chemo/OPDIVO arm had stage IIIC disease, and 2 (1%) patients in the placebo + chemo/placebo arm had stage IV disease.11
§Stage IIA was reported in 7% of patients in the OPDIVO + chemo/OPDIVO arm and 8% of patients in the placebo + chemo/placebo; stage IIB disease was reported in 29% and 27% of patients, respectively.11
IIStage IIIA was reported in 45% of patients in the OPDIVO + chemo/OPDIVO arm and 49% of patients in the placebo + chemo/placebo arm; stage IIIB disease was reported in 19% and 15% of patients, respectively.11
¶N3 node stage was reported in 2 patients (0.9%) in each treatment group.3
#Determined using the PD-L1 IHC 28-8 pharmDx assay (Dako).11
**Includes only Argentina, Australia, Brazil, and Mexico.11