| CHARACTERISTICS | OPDIVO + YERVOY (n=425) | SUNITINIB (n=422) |
|---|---|---|
| Median age, years5,12 ≥65 years, % ≥75 years, % |
62 38 8 |
61 39 7 |
| Male, %5,12 | 74 | 71 |
| IMDC prognostic score, %5,12 Intermediate (1–2) Poor (3–6) |
79 21 |
79 21 |
| No. of sites with ≥1 target/non-target lesion, %5,12 1 ≥2 |
21 79 |
20 80 |
| Quantifiable tumor PD-L1 expression, %5,12 <1% ≥1% |
(n=384) 74 26 |
(n=392) 71 29 |
| Most common site of metastasis, %5,12 Lung Lymph node Bone Liver |
69 45 22 21 |
70 51 23 21 |
OPDIVO Qvantig™ (nivolumab + hyaluronidase-nvhy) is approved as a subcutaneous injection in the monotherapy maintenance phase of treatment

OPDIVO® + YERVOY®:
Unprecedented length of follow-up with 9 years of survival data in 1L aRCC2-4*‡

INDICATION:
OPDIVO® (nivolumab), in combination with YERVOY® (ipilimumab), is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with intermediate or poor risk advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).2,3
OPDIVO QVANTIG™ (nivolumab and hyaluronidase-nvhy), as monotherapy, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with intermediate- or poor-risk advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), following treatment with intravenous nivolumab and ipilimumab combination therapy.1
Limitations of Use: OPDIVO QVANTIG is not indicated in combination with ipilimumab for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma.1
OPDIVO + YERVOY: OS results at primary analysis (median follow-up time of 25.2 months)5
- Median OS was not yet reached (95% CI: 28.2–NE) for OPDIVO + YERVOY and was 25.9 months (95% CI: 22.1–NE) for sunitinib; HR=0.63 (99.8% CI: 0.44–0.89); P<0.00012,5
OPDIVO + YERVOY: OS results at extended follow-up analysis (median follow-up time of 111.1 months)4‡
- The OS rate|| at 108 months for OPDIVO + YERVOY was 30% and 19% for sunitinib. Median OS was 46.7 months (95% CI: 35.0–55.7) for OPDIVO + YERVOY and 26.0 months (95% CI: 21.8–32.6) for sunitinib; HR=0.69 (95% CI: 0.59–0.81)4
*YERVOY was excluded from the trial evaluating subcutaneous administration.1
†Recommended administration time is 3–5 minutes and does not include other aspects of treatment. Actual clinic time may vary.1,6 Must be administered by a healthcare professional.1
‡Based on extended follow-up analysis at a median follow-up time of 111.1 months (range: 103.0–119.3).4
§In a phase 3 trial.5
||OS rates are based on Kaplan-Meier estimates.7
1L=first-line; aRCC=advanced RCC; CI=confidence interval; HR=hazard ratio; I-O=immuno-oncology; NE=not evaluable; OS=overall survival.
INDICATION OPDIVO® (nivolumab), in combination with YERVOY® (ipilimumab), is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with intermediate or poor risk advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
CHECKMATE 214: 1L INTERMEDIATE- OR POOR-RISK ADVANCED RENAL CELL CARCINOMA (aRCC)
Extended Follow-up Data
OPDIVO + YERVOY showed enduring overall survival and a hazard ratio of 0.69 at an unprecedented 9 years of follow-up4*†
9-YEAR MEDIAN FOLLOW-UP: OVERALL SURVIVAL IN ADULT PATIENTS WITH INTERMEDIATE-/POOR-RISK aRCC4†‡

Overall survival rates at follow-up analyses were not pre-specified within the study protocol and were not powered to detect differences between treatment arms.7
In the primary analysis, the pre-specified 12-month overall survival rate was 80% (95% CI: 76–84) with OPDIVO + YERVOY vs 72% (95% CI: 67–76) with sunitinib. The median follow-up time was 25.2 months.5,7
mOS at primary analysis (median follow-up time of 25.2 months)2,5
- OPDIVO + YERVOY: Not yet reached (95% CI: 28.2–NE)2,5
- Sunitinib: 25.9 months (95% CI: 22.1–NE)2,5
- HR=0.63 (99.8% CI: 0.44–0.89); P<0.00012,5
mOS at extended follow-up analysis (median follow-up time of 111.1 months)4
- OPDIVO + YERVOY: 46.7 months (95% CI: 35.0–55.7)4
- Sunitinib: 26.0 months (95% CI: 21.8–32.6)4
- HR=0.69 (95% CI: 0.59–0.81)4
*Based on extended follow-up analysis results at a median follow-up time of 111.1 months (range: 103.0–119.3).4
†OS rates are based on Kaplan-Meier estimates.7
‡Performance status is based on IMDC prognostic score (0=favorable, 1–2=intermediate, 3+=poor).2,4,5
IMDC=International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium.
Select Important Safety Information
Serious Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 214, serious adverse reactions occurred in 59% of patients receiving OPDIVO plus YERVOY (n=547). The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients were diarrhea, pyrexia, pneumonia, pneumonitis, hypophysitis, acute kidney injury, dyspnea, adrenal insufficiency, and colitis.
Common Adverse Reactions
In Checkmate 214, the most common adverse reactions (≥20%) reported in patients treated with OPDIVO plus YERVOY (n=547) were fatigue (58%), rash (39%), diarrhea (38%), musculoskeletal pain (37%), pruritus (33%), nausea (30%), cough (28%), pyrexia (25%), arthralgia (23%), decreased appetite (21%), dyspnea (20%), and vomiting (20%).
Please see additional Important Safety Information below.
Progression-free survival data at 9 years of follow-up4*
9-YEAR MEDIAN FOLLOW-UP: PFS IN ADULT PATIENTS WITH INTERMEDIATE-/POOR-RISK aRCC4†‡

PFS rates at follow-up analyses were not pre-specified within the study protocol and analyses were not powered to detect differences between treatment arms.7
mPFS‡ at primary analysis (median follow-up time of 25.2 months)2,5
- OPDIVO + YERVOY: 11.6 months (95% CI: 8.7–15.5)2,5
- Sunitinib: 8.4 months (95% CI: 7.0–10.8)2,5
- HR=0.82 (99.1% CI: 0.64–1.05)2,5
- Per a pre-specified analysis, PFS did not meet statistical significance
mPFS‡ at extended follow-up analysis (median follow-up time of 111.1 months)4
- OPDIVO + YERVOY: 12.4 months (95% CI: 8.7–16.8)4
- Sunitinib: 8.5 months (95% CI: 7.0–11.1)4
- HR=0.73 (95% CI: 0.61–0.87)4
*Based on extended follow-up analysis results at a median follow-up time of 111.1 months (range: 103.0–119.3).4
†Performance status is based on IMDC prognostic score (0=favorable, 1–2=intermediate, 3+=poor).4,5
‡PFS was assessed by an independent radiographic review committee per RECIST v1.1.2,4,5
NS=not significant.
OPDIVO + YERVOY: More than 4X median DOR vs sunitinib, a TKI therapy, at 9 years of follow-up4*
9-YEAR MEDIAN FOLLOW-UP: DOR IN ADULT PATIENTS WITH INTERMEDIATE- OR POOR-RISK aRCC4†
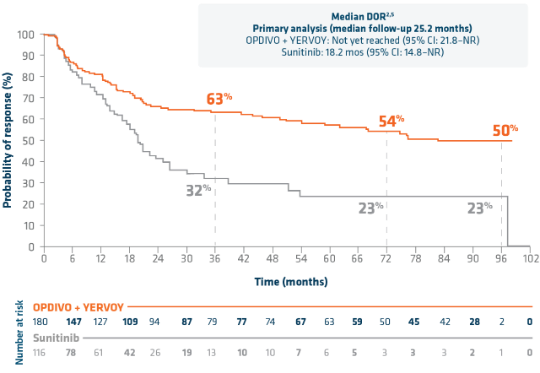
DOR rates at follow-up analyses were not pre-specified within the study protocol and analyses were not powered to detect differences between treatment arms.7
mDOR at extended follow-up analysis (median follow-up time of 111.1 months)4
- OPDIVO + YERVOY: 82.8 months (95% CI: 54.1–NE)4
- Sunitinib: 19.8 months (95% CI: 16.4–26.4)4
- HR=0.48 (95% CI: 0.33–0.69)4
ORR‡ at primary analysis (median follow-up time of 25.2 months)2,5
- OPDIVO + YERVOY: 41.6% (n=177/425 [95% CI: 36.9–46.5]; CR: 9.4% [n=40]; PR: 32.2% [n=137])2,5
- Sunitinib: 26.5% (n=112/422 [95% CI: 22.4–31.0]; CR: 1.2% [n=5]; PR: 25.4% [n=107])2,5
- P<0.0001 for ORR2
ORR‡ at extended follow-up analysis (median follow-up time of 111.1 months)4
- OPDIVO + YERVOY: 42.4% (n=180/425 [95% CI: 37.6–47.2]; CR: 11.8% [n=50]; PR: 30.6% [n=130])4
- Sunitinib: 27.5% (n=116/422 [95% CI: 23.3–32.0]; CR: 2.6% [n=11]; PR: 24.9% [n=105])4
*Based on extended follow-up analysis results at a median follow-up time of 111.1 months (range 103.0–119.3).4
†Based on Kaplan-Meier estimates of duration of response.7
‡ORR was assessed by an independent radiographic review committee per RECIST v1.1.2,4,5
TKI=tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
With OPDIVO + YERVOY, 84.0% of complete responses were ongoing at 9 years of follow-up4*
OPDIVO + YERVOY RESPONSE DATA AT 9 YEARS

ORR† at primary analysis (median follow-up time of 25.2 months)2,5
- OPDIVO + YERVOY: ORR: 41.6% (n=177/425 [95% CI: 36.9–46.5]; CR: 9.4% [n=40]; PR: 32.2% [n=137])2,5
- Sunitinib: ORR: 26.5% (n=112/422 [95% CI: 22.4–31.0]; CR: 1.2% [n=5]; PR: 25.4% [n=107])2,5
- P<0.0001 for ORR2
ORR† at extended follow-up analysis (median follow-up time of 111.1 months)4
- OPDIVO + YERVOY: 42.4% (n=180/425 [95% CI: 37.6–47.2]; CR: 11.8% [n=50]; PR: 30.6% [n=130])4
- Sunitinib: 27.5% (n=116/422 [95% CI: 23.3–32.0]; CR: 2.6% [n=11]; PR: 24.9% [n=105])4
*Based on extended follow-up analysis results at a median follow-up time of 111.1 months (range 103.0–119.3).4
†ORR was assessed by an independent radiographic review committee per RECIST v1.1.2,4,5
A pivotal, phase 3, head-to-head trial vs sunitinib2,5
CHECKMATE 214 STUDY DESIGN2,5
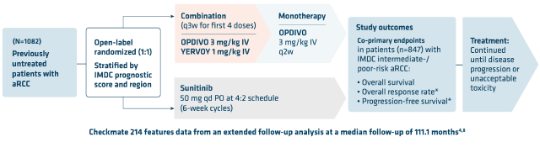
- Short-term induction dosing with OPDIVO + YERVOY during the combination phase followed by OPDIVO monotherapy during the maintenance phase2,5
- Similar to trials reflective of the real-world population, 77% of patients in Checkmate 214 were intermediate-/poor-risk as measured by IMDC5,9-11
- Patients were included regardless of their PD-L1 status. Patients were excluded due to any history of—or concurrent—brain metastases, active autoimmune disease, or medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression2
- Median follow-up for the primary analysis was 25.2 months5
- The safety analysis included 1,082 patients. The efficacy analysis of the co-primary endpoints included 425 patients in the OPDIVO + YERVOY arm and 422 patients in the sunitinib arm5
*In the primary analysis at a median follow-up of 25.2 months, ORR and PFS were assessed by an independent radiographic review committee.2,5
†Checkmate 214 is no longer recruiting.8
IV=intravenous; PD-L1=programmed death-ligand 1; PO=orally; q2w=every 2 weeks; q3w=every 3 weeks; qd=once a day.
Checkmate 214 baseline characteristics2,5
IMDC INTERMEDIATE- OR POOR-RISK PATIENTS

*Of evaluable patients (n=284/384).5
Approximately 75%–80% of 1L aRCC patients qualify as
intermediate or poor risk9†
†Based on large, retrospective, population-based studies.9
No.=number.
Up to 80% of 1L aRCC patients qualify as intermediate or poor risk9*
IMDC RISK FACTORS

Intermediate- or poor-risk patients have ≥1 prognostic risk factor per the IMDC criteria.9
*Based on large, retrospective, population-based studies.9
LLN=lower limit of normal; PS=performance status; ULN=upper limit of normal.
Induction with intravenous OPDIVO + YERVOY followed by OPDIVO Qvantig injection in the monotherapy maintenance phase1,2
OPDIVO is still available as an IV infusion in the monotherapy maintenance phase.1 View OPDIVO IV dosing schedule >

INDICATION OPDIVO Qvantig (nivolumab + hyaluronidase-nvhy), as monotherapy, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with intermediate-or poor-risk advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), following treatment with intravenous nivolumab and ipilimumab combination therapy.
Limitations of Use: OPDIVO Qvantig is not indicated in combination with ipilimumab for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma.
- The first dose of OPDIVO Qvantig monotherapy should be administered after completing 4 doses of the OPDIVO and YERVOY combination therapy1,2
- Review the Full Prescribing Information for OPDIVO, OPDIVO Qvantig, and YERVOY for recommended dosage information
- No premedications required with OPDIVO + YERVOY or OPDIVO Qvantig1-3
*OPDIVO is administered as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes.2
†YERVOY is administered as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes.3
‡OPDIVO Qvantig is administered as a 3- to 5-minute subcutaneous injection.1
q4w=every 4 weeks.

Safety Data
View a selected safety profile of adverse reactions seen in clinical trials.

Dosing Schedules
Find dosing information to get patients started on therapy.

Another Advanced RCC Option
Learn more about another OPDIVO-based combination for advanced renal cell carcinoma.
See OPDIVO + YERVOY dual I-O efficacy data in multiple tumor types
References:
- OPDIVO Qvantig [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company.
- OPDIVO [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company.
- YERVOY [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company.
- Choueiri TK, Escudier B, McDermott DF, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab vs sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: Final analysis from the phase 3 CheckMate 214 trial. Oral Presentation at ASCO; May 30–June 3, 2025; Chicago, IL.
- Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, et al; for CheckMate 214 Investigators. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(14):1277-1290.
- Albiges L, Bourlon MT, Chacón M, et al. Subcutaneous versus intravenous nivolumab for renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2025;36(1):99-107.
- Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, et al; for CheckMate 214 Investigators. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(14):1277-1290 [protocol].
- Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02231749. Accessed October 11, 2022.
- Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, et al. External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(2):141-148.
- Ko JJ, Xie W, Kroeger N, et al. The International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium model as a prognostic tool in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma previously treated with first-line targeted therapy: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(3):293-300.
- Yip SM, Wells C, Moreira R, et al. Real world experience of immuno-oncology agents in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results from the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC). Poster presentation at ASCO GU 2017. Abstract 492.
- Data on file. NIVO 441. Princeton, NJ: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2019.